Learn Cloud Computing - Step by Step Guide
What is Cloud Computing?
Why Cloud Computing?
How does Cloud computing work?
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
Advantages and Disadvantages
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud Service Providers in Market
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud traditionally depicts the internet, hence, it is also referred to as “the cloud”. In simple terms, it means saving or accessing your data and programs over the internet.
Cloud computing means making computer infrastructure and services available as per need using internet. The infrastructure could include storage space, development IDE, database, computing power or complete software applications. To use these resources from the cloud vendors, organizations do not have to make any massive capital expenditures. The billing model of cloud computing is similar to the electricity bill payment we do based on our consumption at home. Nowadays, almost everything is moved to the cloud, running in the cloud, accessed from the cloud and even stored in the cloud.
So, we may wonder where exactly is this cloud located? Well, we can say, it is somewhere at the other end of your internet connection where you can store your files that can be accessed from anywhere in the world.
Cloud has made a huge difference to organizations, primarily because of three reasons:
- You do not have to maintain or monitor any infrastructure for the same.
- It will never run out of capacity, since it is scalable and virtually infinite.
- You can access your cloud based applications remotely anytime, you just need a device which can connect to the internet.
Now that we have an idea of what cloud is, do you know how much of our daily online activities is based on cloud? All our social media interactions are all on the cloud, anything that we store online, or buy online pay online bills, everything is on cloud!
Many services have emerged in the last decade or so that allows end-users to save/update information without paying any charges, in advance. These are typically consumer oriented services. Twitter, Wikipedia, youtube, facebook, linkedin, Google docs and blogger all are examples of cloud computing. Google and Microsoft provide development platforms that can be accessed using “pay-per-use” billing model. Amazon.com was one of the first few vendors to provide cloud computing services like storage space and computing resources.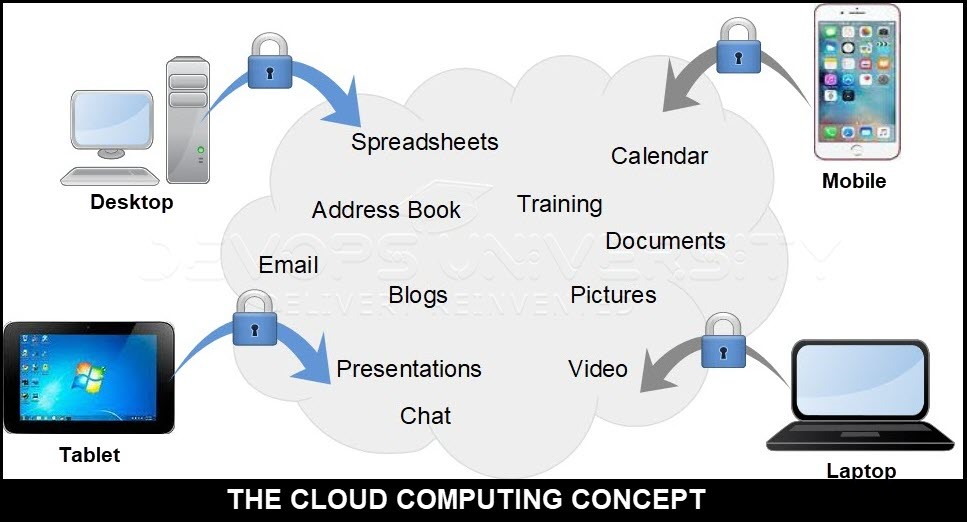
Why Cloud Computing?
For any IT company, we need a Server Room as its the basic need of IT organizations.
There should be a database server, mail server, networking, firewalls, routers, modem, switches, configurable system, high internet bandwidth and maintenance engineers, all should be present in the server room. In establishing such an IT infrastructure, a huge financial cost is involved.
So, to overcome all these issues and to minimize the infrastructure cost, Cloud Computing came into existence. It facilitates smaller organizations to access computing infrastructure without making any significant initial investment.
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
Let us understand through an example. Assume that you are an executive at an organization where its your responsibility that all employees have the right hardware and software they need to do their work. You have to take care of buying the new computers as well as purchasing software, licenses etc and make them available to employees as and when needed. Whenever there are new joinees, your current license should be able to accommodate a new user. All these tasks can be stressful and involve huge financial cost.
Now instead of installing a suite of software on each computer, you just need to load one application which will allow the employees to login into a Web-based service. which will host all the programs required by the user for his/her task. Remote servers running elsewhere, have the power to run everything from emails to word processing to complex data analysis programs, all due to cloud computing. The only thing the user’s computer will require is to be able to run the cloud computing interface software, which can be a simple Web browser and the rest would be taken care of by cloud.
Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- Agility: The cloud works in a distributed computing environment where resources are shared among users and it works very fast.
- High reliability: The number of servers available are high and reliable and there is reduced probability of hardware failures or infrastructure issues.
- High Scalability: Peak loads can be easily managed without any human intervention as there is “on-demand” provisioning of resources on a large scale.
- Pay-per-use mode: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are available for users to access cloud services and pay the charges only for the availed services.
- Shared Resources: With the help of cloud computing, multiple users and applications can share common infrastructure which makes the work more efficient and cost-effective. IT organizations don’t need to set up their own infrastructure and can pay for the remotely available resources, according to their usage.
- Device and Location Independence: Cloud computing allows the users to access resources , regardless of their location or what device they use. As infrastructure is remote and accessed via the Internet, users can connect from anywhere.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
- No need for a high configured machine
You don’t require a high configuration computer to run web-based applications because applications run on cloud, not on your local machine. - Lower IT infrastructure cost
There is no need to invest in a huge number of powerful servers or the IT staff for maintenance of the same. - Reduced software-related costs
The need to buy separate software packages for each machine in the organization, is eliminated in the cloud computing scenario. Another advantage is that users don’t face issues due to obsolete software or bear high software upgradation costs. Since the update happens automatically, they are available to the user when he logs in the next time. - Increased computing power
Since, the execution capacity of cloud servers are very high, the application performance is extremely fast. - Unlimited storage capacity
There is a huge amount of storage capacity like 2000 GB or even more if required, available on cloud.

Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
- Require a constant high-speed Internet Connection
A constant high speed network is a must to avail the benefits of cloud computing. - Data Security
With cloud computing, all your data resides on the cloud. This imposes a huge security risk due to unauthorized access.
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing can be categorized in two ways:
- Deployment Models
- Service Models

1. Deployment Models
Based on how it is located, cloud computing can be classified in the following three ways:
- Public cloud
A cloud platform based on the standard cloud computing model in which vendors offer resources, applications storage to consumers over the internet is called as public cloud computing. The hardware resources in public cloud are shared among multiple users and are accessible over a public network. Startups having budget constraints, or organizations where high security is not a priority opt for Public Cloud Computing to save money. Here, the computing infrastructure is hosted by the cloud vendor at the vendor’s premises. The customer has no visibility and control over the location of the host computing infrastructure.
Advantages
- It offers greater scalability
- Its cost effectiveness helps you save money.
- It is reliable as no single point of failure will interrupt your services.
- SaaS, (Paas), (Iaas) are available on Public Cloud platform easily
- No dependency on location
Disadvantages- No control over privacy or security
- Not apt for applications handling sensitive data
- Lacks flexibility as the platform depends on the vendor
- No strict data management protocols
- Private Cloud
A secure cloud environment where the computing infrastructure is dedicated to a single organization only and not shared with other organizations. The additional security allows companies to keep confidential and sensitive data in the private cloud environment.Private clouds are of two types:
- On-premise private clouds
- Externally hosted private clouds
Externally hosted private clouds are exclusively used by a single organization, but are hosted by a third party cloud provider. They are cheaper than On-premise private clouds.Advantages
- Greater Security and Privacy
- Greater control over system configuration according to company’s need
- Reliable performance
- Enhanced quality of service
- Cost effective
Disadvantages- Expensive as compared to public cloud
- Requires IT Expertise
Hybrid Cloud
In this computing model, a combination of both public and private cloud is used. In this model, companies can use public cloud for non-confidential data transfer and switch to private cloud for sensitive data transfer or hosting of critical applications.
This helps companies achieve maximum efficiency and deliver better results to clients.
It is gaining popularity in many business, as it gives the benefits of both the models.
Advantages
- It is scalable
- It is cost efficient
- Offers better security
- Offers greater flexibility
Disadvantages- Infrastructure Dependency
- Possibility of security breach through public cloud

2. Service Models
Based upon the services offered, clouds are classified in the following 3 ways:
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS)
offers hardware related services through cloud computing. These include storage services (database or disk storage) or virtual servers.
It provides access to primary resources like physical machines, virtual machines, virtual storage, IP addresses, VLANs etc.
All of the resources mentioned above are available to the end users through server virtualization. Customers access these resources as if they own them.Characteristics
- Automated administrative tasks
- Dynamic scaling
- Platform virtualization
- Internet connectivity
Benefits- Users with admin rights on VMs have full control over computing resources
- Flexible and efficient renting of computer hardware
- Portable and interoperable with legacy applications
IssuesIaaS, PaaS and SaaS have common issues like network dependency and browser based risks. IaaS also has some specific issues, like:
- Compatibility with legacy security vulnerabilities
- Virtual Machine sprawl
- Robustness of VM-level isolation
- Data erase practices
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)
offers the runtime environment for applications. It also offers the tools required for development and deployment of applications. PaaS has a point-and-click tool feature that enables even non-developers to create web applications. Some of the major PaaS providers are Google’s Application Engine, Microsoft’s Azure, Salesforce.com’s force.com. Developer may log on to these websites and use the built-in API to create web-based applications.
Characteristics
- Browser based development environment.
- Built-in security, scalability and web service interfaces.
- Workflow, approval processes, and business rules.
- Easy integration with other applications on the same platform.
Benefits- Lower administrative overhead
- Lesser ownership cost
- Scalable solutions
- More current system software
Issues- Significant burdens on customer’s browsers to maintain
- connections to the provider’s machines
- Lack of portability between PaaS clouds
- Event based processor scheduling
- Security engineering of PaaS applications
Software-as–a-Service (SaaS)
model provides software applications as a service to the users. It refers to a software which is deployed on a host service and is accessible through Internet. Software as a service (SaaS) includes a complete software offering on the cloud. Users can access a software application hosted by the cloud vendor on pay-per-use basis. The first in this field was Salesforce.coms online Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and some other examples include Google’s gmail and Microsoft’s hotmail, Google Docs and Microsoft’s online version of office.
There are several SaaS applications listed below:
- Billing and invoicing systems
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) applications
- Help desk applications
- Human Resource (HR) solutions
Some of the SaaS applications are not customizable like Microsoft Office Suite, but SaaS provides Application Programming Interface (API), which the developers use to customize an application.Characteristics
- SaaS makes the software available over the Internet.
- The software applications are supported by the vendor.
- The license to the software may be subscription based or usage based
- Billing is on a recurring basis.
- SaaS applications are cost-effective as there is zero maintenance at the user end.
- Available on demand.
- Scalable on demand.
- Automatic updates.
- SaaS offers shared data model where multiple users can share a single infrastructure instance.
- All users run the same version of the software.
BenefitsUsing SaaS is beneficial in terms of scalability, efficiency and performance.
Some of the benefits are:
- Modest software tools
- Efficient use of software licenses
- Centralized management and data
- Platform responsibilities managed by provider
- Multi Tenant solutions
Issues- Browser based risks
- Network dependence
- Lack of portability between SaaS clouds

Open SaaS and SOA(Service-oriented architecture)
Open SaaS uses SaaS applications, which are developed using open source programming language. These SaaS applications can run on any open source operating system and database. Open SaaS has several benefits listed below:
- No License Required
- Low Deployment Cost
- Less Vendor Lock-in
- More portable applications
- More Robust Solution
Cloud Service Providers In Market
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- AWS is the safest cloud service platform offering a wide range of infrastructure services like database storage, computing power, networking etc.
- By using AWS, Users
 are able to build scalable, complicated and flexible applications, using AWS.
are able to build scalable, complicated and flexible applications, using AWS. - One can experience AWS and do hands-on using free-tier services.
2. Kamatera
- Kamatera provides very
 high-performance and low-maintenance and cloud infrastructure services.
high-performance and low-maintenance and cloud infrastructure services. - The cost is very low for their cloud services.
- They charge only according to what you use.
- There is no penalty to add or remove servers
- 99.95% uptime is guaranteed.
- There is a 30-day free trial.
3. Microsoft Azure
- It is used for deploying,
 designing and managing the applications through a worldwide network.
designing and managing the applications through a worldwide network. - Was known as Windows Azure, previously.
- Supports various operating systems, databases, tools, programming languages and frameworks etc.
- A free trial for 30 days is available.
4. Google Cloud Platform
- GCP uses resources
 located at Google data centers.
located at Google data centers. - GCP is an integrated storage for live data, used by developers and enterprises.
- Apart from the free trial, GCP offers various flexible Pay-As-You-Go payment plans.
5. Adobe
- Adobe offers many cloud products like
 Adobe Creative Cloud, Adobe Experience Cloud and Adobe Document Cloud etc.
Adobe Creative Cloud, Adobe Experience Cloud and Adobe Document Cloud etc. - Adobe Creative Cloud service is a SaaS, offering its users, access Adobe tools like editing the videos, photography, graphic designing etc.
- Adobe Experience Cloud provides access to a broad set of advertising, campaign building and business intelligence solutions.
- Adobe Document Cloud is a complete digital documentation
- solution
6. Vmware
- It is a universal leader in virtualization and Cloud
 Infrastructure.
Infrastructure. - VMware vCloud Air is a safe and protected public cloud platform offering networking, storage, disaster recovery and computing etc.
- VMware’s Cloud solutions help organizations maximize their cloud computing profits by combining the services, technologies, guidance needed to operate and manage the staff etc.
7. IBM Cloud
- IBM Cloud offers all cloud delivery services – Iaas, PaaS, and SaaS.

- IBM Cloud gives the freedom to the users to choose and combine the desired tools, data models and delivery models in designing and creating next-generation services or applications.
- IBM Cloud is used to build pioneering way outs that can gain value for your business and industry.
8. Rackspace
- Rackspace Cloud offers a many cloud computing services like
 hosting web applications, Cloud Files, Cloud Block Storage, Cloud Backup, Databases and Cloud Servers etc.
hosting web applications, Cloud Files, Cloud Block Storage, Cloud Backup, Databases and Cloud Servers etc. - Rackspace Cloud Block Storage uses solid-state drives and hard drives, in combination, to deliver high performance.
- Rackspace Cloud Backup provides file-level backups with low cost, uses compression and encryption techniques.
9. Red Hat
- It is an Open Cloud technology that
 provides agile and flexible solutions to IT companies.
provides agile and flexible solutions to IT companies. - We can modernize, update and manage the applications from a single point and integrate all the desired aspects into a single solution, using Red Hat Cloud.
- Red Hat Cloud Infrastructure helps us in building and managing a cost-effective, open cum private cloud.
10. Salesforce
- Salesforce Cloud Computing offers all the business applications
 like CRM, ERP, customer service, sales, mobile applications etc.
like CRM, ERP, customer service, sales, mobile applications etc. - Salesforce cloud computing comprises of multiple cloud services like Sales Cloud, Service Cloud, Marketing Cloud etc.
- Salesforce Sales Cloud helps in managing the customer’s contact information and automating the business processes etc.
11. Oracle Cloud
- Oracle Cloud is available
 as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS.
as SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS. - Oracle Cloud helps the organizations in transforming their business and reducing IT Complexity.
- Oracle Cloud SaaS is a complete data-driven and secure cloud environment.
- Oracle Cloud PaaS aids IT Enterprises and individual developers to develop, connect, protect and share data across the applications.
- Oracle Cloud IaaS is a wide set of subscription-based, integrated services.
12. SAP
- SAP Cloud Platform is
 an enterprise service with a wide range of application development services.
an enterprise service with a wide range of application development services. - SAP has powerful business networks, cloud collaboration, and advanced IT security, and hence it is considered as the best cloud provider.
- SAP has a universal foundation named SAP HANA, for its cloud services.
- SAP Cloud Platform is modernizing the way enterprises work on iPhone and iPad.
13. Dropbox
- Dropbox is a cloud storage service used by
 small businesses and customers to store artifacts virtually on remote cloud servers.
small businesses and customers to store artifacts virtually on remote cloud servers. - Generally, Dropbox serves as an online personal hard drive.
- Through Dropbox, users can access any saved data or content from any device using an internet connection.
- Dropbox can be downloaded as a desktop app and you can save the files directly in the Dropbox folder located on your desktop.
